The war between Android vs iOS app development has been going on for years. Each option has its strengths and weaknesses based on programming languages, development environments, design, complexity, market share, and many others.
This article will dive into the key differences between developing for Android vs iOS, including aspects like:
- programming languages used;
- development tools and environment;
- platform-specific design considerations;
- the overall complexity of development;
- market share and monetization potential.
We will also discuss the expenses and time required to create apps for each platform. Last but not least, we will conclude the article and highlight the main points to help you determine whether it is worth involving Android or iOS mobile game development services for your next mobile application.
What Is iOS?
iOS is an Apple-developed mobile operating system and is used in all iPhone and iPad products. The native iOS applications are developed in Objective-C or Swift languages to be compatible with iOS devices.
The iOS platform is much more restricted and controlled, as Apple controls the distribution of applications and systems updates. Applications developed for the iOS platform can only be installed via the proprietary App Store. Originally developed for the iPhone, iOS was soon adapted to the iPad and the iPod Touch. Other devices, such as the Apple TV and Apple Watch, also use versions of the iOS operating system.
As a result of Apple’s strict adherence to the quality of its devices and the experience of its users, iOS customers are more likely to pay for applications than their Android counterparts. There is also the iOS developer environment and documentation which makes iOS vs Android development relatively smoother.
What Is Android?
Android is an open-source mobile platform developed by Google for mobile devices. It is currently the most-used OS globally across devices of different manufacturers, including Samsung, Xiaomi, Oppo, Sony, etc.
Android apps developed natively are usually coded in Java or Kotlin and built using Android SDK and Android Studio. Android applications can be published in various app stores such as Google Play store, Samsung Galaxy store, Amazon app store, and others.
The open-source nature of Android has resulted in significant device fragmentation over the years. Developers need to account for and test against hundreds of Android device types with varying capabilities and screen sizes. However, the large user base also presents significant revenue potential across global markets.
Differences Between iOS vs Android App Development
Now that we’ve provided a basic overview of the two dominant mobile platforms, let’s explore some of the key differences between native iOS vs Android app development:
Programming Languages
The official programming languages for each platform are:
- iOS – Swift and Objective-C
- Android – Java and Kotlin
Swift is a language designed by Apple and has been in use for a comparatively shorter period than Objective-C. Kotlin is a relatively new language that is backed by Google as a better option for developing Android applications than Java.
Is iOS development easier than Android? No, developers require learning Apple’s Objective-C or Google’s Java for iOS or Android development. This is because the knowledge acquired from one platform cannot be transferred to the other platform.
Development Environment
iOS developers use Xcode IDE with a number of built-in iOS SDKs, simulators, and other tools for Android apps vs Apple apps. Everything is neatly packaged to streamline iOS development.
Android developers download Android Studio to start developing. They also need to separately install desired SDK versions, emulators, build tools etc. The fragmented nature of Android makes setting up the dev environment more tedious.
Apple offers limited ways to test and debug iOS apps during development, while Android Studio provides a richer set of testing tools. Xcode’s emulator experience and stability are better than those of the Android emulator.
System-Specific Design Difference Between iOS and Android Development
iOS provides standardized UI elements and strict Human Interface Guidelines that ensure consistency across Android apps vs Apple apps. Android offers more flexibility, but developers must put extra effort into ensuring compliance with Material Design principles across device types.
Android allows greater customization of hardware features like notifications LEDs, custom vibrations, etc. iOS provides limited system access and focuses on battery life optimization. Navigation flows also vary based on platform conventions.
Development Complexity
iOS app development generally has a smoother learning curve. Tighter hardware and software integration allows developers to optimize and test with confidence. Publishing apps also involves simple uploads to the App Store for review.
Android app development is comparatively more complex due to device fragmentation, multiple app stores, and no standard for OS updates. Devices from smaller manufacturers may also not conform to compatibility guidelines.
Market Share
As per StatCounter GlobalStats, the global mobile OS market share in May 2024 is:
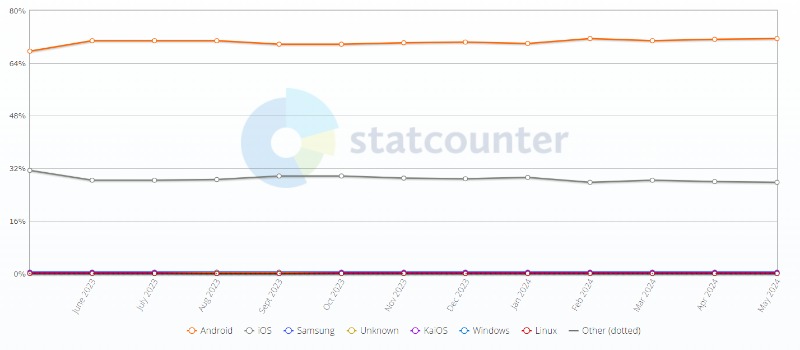
- Android: 71.5%
- iOS: 27.73%
So, Android clearly dominates in terms of install base worldwide. Apple has a majority market share in only a few geographies, like North America and Western Europe. However, iOS generates much higher revenue per user.
While Android offers a wider reach, especially in emerging markets, iOS monetization cannot be ignored due to the affluent user profile.
Cost of Creating Mobile Game Apps: iOS vs Android
A key consideration for most developers is the total cost and effort involved in building an app or game for iOS versus Android.
Let’s analyze how much does it cost to make a mobile game – typical factors:
- Development Costs. Android app development takes more effort due to device compatibility testing. iOS allows developers to focus on the latest 2-3 device generations. Android app development costs can be 20-25 percent higher on average.
- Testing Costs. iOS apps need testing mainly on iPhone and iPad variants. Android requires testing across many more device types with varying capabilities. More extensive compatibility testing increases QA costs.
- Design Costs. iOS apps share common design elements, so minimal design customization is usually enough. The adoption of material design is not consistent in Android devices; therefore, the costs of designing are relatively higher.
- Distribution Costs. To publish iOS apps on the App Store, a developer has to obtain a membership, which costs $99 per year. iOS developer vs Android developer apps can be free across the various stores but may require store-specific optimization.
- Maintenance Costs. Android OS is fragmented, and as a result, developers have to target older Android versions, which increases app maintenance costs compared to iOS apps.
In general, it is believed that the cost of creating an Android app for the same functions is at least 25-30% higher on average compared to iOS apps. However, due to its open platform nature, Android should be able to attract more customers to its services and thus make up for the costs.
Return on Investment
The comparison of the ROI of mobile Android apps vs Apple apps is based on the monetization of the applications, as well as the revenue figures from both platforms.
Paid Apps/Games
iOS users are willing to spend more on applications than Android users in all the segments. Consumers on iOS pay almost twice as much per download for some categories.
In-App Purchases:
App store sales in iOS are almost double the overall number worldwide, even though the users are comparatively fewer. The number of transactions is also significantly different, and the average transaction value is much higher.
Advertising
The eCPM rates on iOS are over 4x higher because of the overall valuable user demographics. More click-through rates also result in better monetization.
Still, although Android’s market share is greater worldwide, iOS is still leading in-app monetization indicators. Apple’s ecosystem is a strong one – it has a devoted and well-to-do audience that drives the revenues.
Another factor is the easy discoverability of the app within the carefully selected App Store and multiple possibilities to pay for the service.
iOS or Android: What to Choose?
The Android vs iOS development choice depends on multiple aspects like budget, target market, features, monetization goals, etc.
Here is a summary of key factors that can guide the decision-making:
- Development Costs. Android apps require higher investment but allow scaling to global markets
- Time-to-Market. iOS app vs Android app can be launched 15-20% faster on average
- Design Considerations. iOS allows a streamlined UI/UX design process
- Feature Availability. Android apps can leverage more device capabilities
- Audience Reach. Android is better for targeting emerging markets
- Monetization Potential. iOS delivers higher revenues through app purchases and in-app payments
- App Maintenance. iOS apps require less effort for post-launch support
For most apps targeting Western audiences, iOS continues to provide higher monetization potential. Apps focused on global reach across wider demographics are better suited for the Android platform.
Comparing Android vs iOS Game Development
The game app sector raises awareness of the difference in monetization of the platforms.
According to Apple, iOS game developers make about x2 more in revenue than Android game developers. According to Techreport, mobile game downloads are higher worldwide on the Google Play Store for games.
Apple provides a wide range of APIs and services for games such as Game Center, iCloud, controller, etc iOS games have the advantage of having predictable hardware and OS versions.
However, the cross-platform Android vs iOS game development is beneficial in terms of cost to the game developers in terms of development tools and distribution. The Unity game engine is easy to use and has a range of features that make cross-platform development possible. Google Play also offers several monetization options, such as advertising and paid products.
For the majority of game developers who aim to reach the Western audience, iOS seems to be the safer option to start with. Android can be considered for increasing reach in international markets.
Conclusion
The decision to develop for the Android vs iPhone can be made based on the importance of the different priorities in the technical and business sense that are applicable to the application.
Android has better market reach, especially in the developing world since the cost of smart devices has continued to reduce. But still, on average, iOS is ahead in the financial aspect due to its users who will pay for the applications.
When it comes to decision-making between iOS vs Android development, iOS has a shorter time to market, fewer tools, and no device factors to be concerned about. It is also noteworthy that the consistent release processes minimize go-live risks.
The Android platform is more flexible in terms of technical and distribution aspects. Due to device fragmentation, customers also incur additional expenses relative to testing and maintenance.
Therefore, for apps targeting mature Western markets and looking forward to offering the best user experience, iOS remains the best for now. Android is preferable for startups that aim to solve global issues for a larger audience across a larger population using a larger variety of devices.










